A Comprehensive Review on Nasal Drug Delivery System
Keywords:
Nasal drug delivery, Intranasal route, Nanoparticles, Mucoadhesive systems, BioavailabilityAbstract
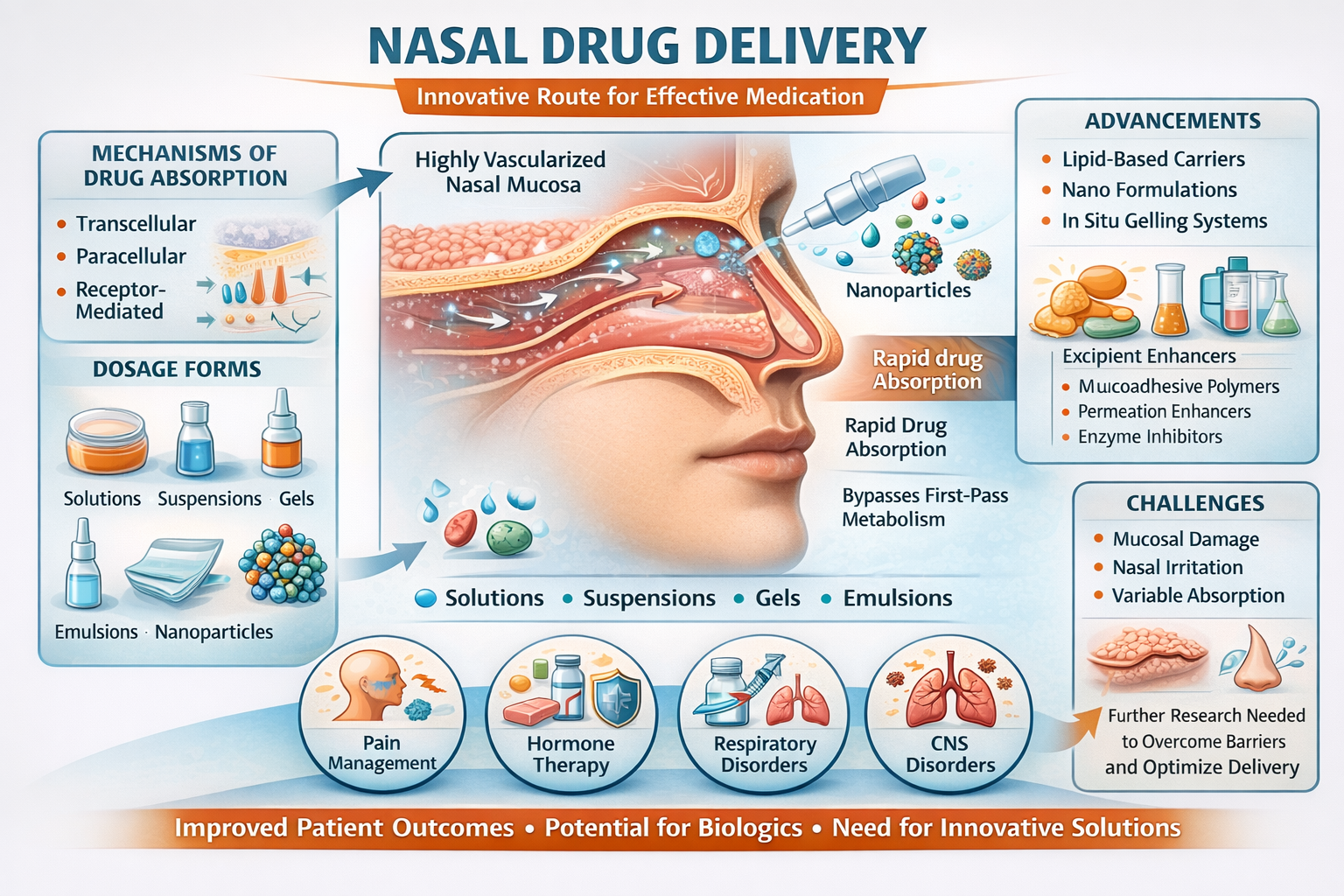
Nasal drug delivery has developed as a promising alternative route for the administration of both systemic and local medications, due to its non-invasive nature, rapid onset of action, and potential to bypass first-pass metabolism. Drug absorption is made easier by a mucosal surface that is highly vascularized in the nasal cavity. The nasal cavity offers a highly vascularized mucosal surface, facilitating drug absorption through various mechanisms, including transcellular, paracellular, and receptor-mediated transport. To improve bioavailability and extend drug retention in the nasal mucosa, numerous dosage forms, including solutions, suspensions, gels, emulsions, nanoparticles, and microparticles, have been developed. To enhance drug absorption and stability, excipients like mucoadhesive polymers, permeation enhancers, and enzyme inhibitors are included. However, advanced formulation strategies, such as lipid-based carriers, nano formulations, and in situ gelling systems, are required to address issues like mucociliary clearance, enzymatic degradation, and limited drug permeability. Pain management, hormone therapy, vaccine administration, and the treatment of respiratory and central nervous system (CNS) disorders are just a few examples of the many therapeutic applications of nasal drug delivery. Due to the possibility of enhanced systemic absorption, intranasal delivery of biologics like proteins and peptides has also received attention. Nasal drug delivery has some drawbacks, including the possibility of mucosal damage with long-term use, nasal irritation, and variability in drug absorption due to physiological conditions. Further research is needed to overcome these challenges through innovative formulations and delivery technologies. Overall, nasal drug delivery remains a highly promising and evolving field with significant potential for improved patient outcomes and therapeutic efficacy.
Downloads
References
Hickey, A. J. (2004). Pharmaceutical inhalation aerosol technology (2nd ed.). Marcel Dekker.
Illum, L. (2003). Nasal drug delivery—Possibilities, problems and solutions. Journal of Controlled Release, 87(1–3), 187–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-3659(02)00368-6
Ugwoke, M. I., Verbeke, N., & Kinget, R. (2001). The biopharmaceutical aspects of nasal mucoadhesive drug delivery. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 53(1), 3–21. https://doi.org/10.1211/0022357011775230
Arora, P., Sharma, S., & Garg, S. (2002). Permeability issues in nasal drug delivery. Drug Discovery Today, 7(18), 967–975. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6446(02)02452-2
Singh, A. K., Singh, A., & Madhav, N. V. S. (2012). Nasal cavity: A promising transmucosal platform for drug delivery and research approach from nasal to brain targeting. Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics, 2(3), 22–33.
Chirag, P., Tyagi, S., Mangukia, D., Ishita, S., Shreya, P., & Pinkesh, P. (2013). A recent review on alternative system of parenteral delivery: Nasal drug delivery system. Journal of Drug Discovery and Therapeutics, 1, 12–18.
Dale, O., Nilsen, T., Loftsson, T., Tønnesen, H. H., Klepstad, P., Kaasa, S., Holand, T., & Djupesland, P. G. (2006). Intranasal midazolam: A comparison of two delivery devices in human volunteers. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 58(10), 1311–1318. https://doi.org/10.1211/jpp.58.10.0005
Ozer, Y. A. (1990). The importance of intranasal route for application of drugs and nasal drug delivery systems. Turkish Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 30(3), 136–147.
Chajed, S., Sangle, S., & Barhate, S. (2011). Advantageous nasal drug delivery system: A review. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research, 2(6), 1322–1336.
Zaheer, A., Sachin, & Swamy, N. G. N. (2012). Mucoadhesive polymers: Drug carriers for improved nasal drug delivery. Indian Journal of Novel Drug Delivery, 4(1), 2–16.
Illum, L. (1996). Nasal delivery: The use of animal models to predict performance in man. Journal of Drug Targeting, 3, 427–442.
Ravikumar, R., Balan, R., Ganesan, N., & Thiruvengadam, D. (2015). Recent modalities in drug delivery via inhalation therapy – An advanced treatment strategy for pulmonary carcinoma. International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 7, 8–21.
Behl, C., Pimplaskar, N. K., Sileno, A. P., Demeireles, J., & Romeo, V. D. (1998). Effect of physicochemical properties and other factors on nasal drug delivery. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 29, 89–116.
Hickey, J. (2004). Pharmaceutical inhalation aerosol technology (2nd ed.). Marcel Dekker.
Alagusundaram, M., Deepthi, N., Ramkanth, S., Angalaparameswari, S., Saleem, T. S. M., Gnanaprakash, K., Thiruvengadarajan, V. S., & Chetty, C. M. (2010). Dry powder inhalers—An overview. International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, 1(1), 34–42.
Sharma, P. K., Chaudhari, P., Kolsure, P., Ajab, A., & Varia, N. (2006). Recent trends in nasal drug delivery system—An overview. Advance Research in Pharmaceuticals and Biologicals, 5, 1–4.
Arora, P., Sharma, S., & Garg, S. (2002). Permeability issues in nasal drug delivery. Drug Discovery Today, 7(18), 967–975.
Aulton, M. E. (2002). Pharmaceutics: The science of dosage form design (2nd ed.). Churchill Livingstone.
Aurora, J. (2002). Development of nasal delivery systems: A review. Drug Delivery and Technology, 2(7), 1–8.
Bawarshi, R. N., Hussain, A., & Crooks, P. A. (1989). Nasal absorption of 17α-ethinyloestradiol in the rat. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 41, 214–215.
Bernstein, J. M., Reddy, M. S., Scannapieco, F. A., Faden, H. S., & Ballow, M. (1997). The microbial ecology and immunology of the adenoid: Implications for otitis media. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 830, 19–31.
Buri, P. (1966). Hydrogels destinés à la muqueuse nasale. Pharmaceutica Acta Helvetiae, 41, 88–101.
Chien, Y. W., Su, K. S. E., & Chang, S. F. (1989). Nasal systemic drug delivery. In Marcel Dekker series on drug delivery (pp. 1–77). Marcel Dekker.
Chien, Y. W., & Chang, S. F. (1987). Intranasal drug delivery for systemic medications. Critical Reviews in Therapeutic Drug Carrier Systems, 4, 67–194.
Corbo, D. C., Liu, J. C., & Chien, Y. W. (1990). Characterization of the barrier properties of mucosal membranes. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 79, 202–206.
Dodane, V., Khan, M. A., & Merwin, J. R. (1999). Effect of chitosan on epithelial permeability and structure. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 182, 21–32.
Donnelly, A., Kellaway, I. W., Taylor, G., & Gibson, M. (1998). Absorption enhancers as tools to determine the route of nasal absorption of peptides. Journal of Drug Targeting, 5, 121–127.
Durrani, Z., McInerney, T. L., McLain, L., Jones, T., Bellaby, T., Brennan, F. R., & Dimmock, N. J. (1998). Intranasal immunisation with a plant virus expressing a peptide from HIV-1 gp41. Journal of Immunological Methods, 220, 93–103.
Edman, P., Björk, E., & Ryden, L. (1992). Microspheres as a nasal delivery system for peptide drugs. Journal of Controlled Release, 21, 165–172.
Finlay, W. H. (2001). The mechanics of inhaled pharmaceutical aerosols. Academic Press.
Upadhyay, S., Parikh, A., Joshi, P., Upadhyay, U. M., & Chotai, N. P. (2011). Intranasal drug delivery system—A glimpse to become maestro. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science, 1(3), 34–44.
Gizurarson, S., & Bechgaard, E. (1991). Intranasal administration of insulin to humans. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 12, 71–84.
Hardy, J. C., Lee, S. W., & Wilson, C. G. (1985). Intranasal drug delivery by spray and drops. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 37, 294–297.
Harris, A. S., Nilsson, I. M., Wagner, Z. G., & Alkner, U. (1986). Intranasal administration of peptides. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 75, 1085–1088.
Hirai, S., Yashiki, T., & Mima, H. (1981). Effect of surfactants on nasal absorption of insulin in rats. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 9, 165–171.
Hofstee, B. H. (1952). Specificity of esterase II. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 199, 365–371.
Hughes, B. L., Allen, D. L., Dorato, M. A., & Wolff, R. K. (1993). Effect of devices on nasal deposition and mucociliary clearance in rhesus monkeys. Aerosol Science and Technology, 18, 241–249.
Hussain, A., Hamadi, S., Kagoshima, M., Iseki, K., & Dittert, L. (1991). Does increasing the lipophilicity of peptides enhance their nasal absorption? Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 80, 1180–1181.
Hussain, A. A., Hirai, S., & Bawarshi, R. (1981). Nasal absorption of progesterone in rats. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 70, 466–467.
Hussain, A. A., Hirai, S., & Bawarshi, R. (1979). Nasal absorption of propranolol in rats. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 68, 1196–1199.
Hussain, A. A., Foster, T., Hirai, S., Kashihara, T., Batenhorst, R., & Jones, M. (1980). Nasal absorption of propranolol in humans. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 69, 1240–1243.
Hussain, M. A., Koval, C. A., Shenvi, A. B., & Aungst, B. J. (1990). Recovery of rat nasal mucosa from the effects of aminopeptidase inhibitors. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 79, 398–400.
Illum, L., Mathiowitz, E., Chickering, D. E., & Lehr, C. M. (2011). Advantageous nasal drug delivery system: A review. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research, 2(6), 1322–1336.
Parvathi, M. (2012). Intranasal drug delivery to brain: An overview. International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Chemistry, 2(3), 889–895.
Hardy, J. G., Lee, S. W., & Wilson, C. G. (1985). Intranasal drug delivery by spray and drops. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 37, 294–297.
Rudman, K. L., O’Brien, E. K., & Leopold, D. A. (2011). Radiographic distribution of drops and sprays within the sinonasal cavities. American Journal of Rhinology & Allergy, 25, 94–97.
Mahalaxmi, R., Kumar, D. S., & Shirwaikar, A. (2007). Preparation of mucoadhesive microspheres for nasal delivery by spray drying. Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 69, 651–657.
Mosab, A. (2025). Approaches to achieve an oral controlled release drug delivery system using polymers: A recent review. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 7, 16–21.
Giuliani, A., Balducci, A. G., Zironi, E., Colombo, G., Bortolotti, F., & Lorenzini, L. (2018). In vivo nose-to-brain delivery of ribavirin. Drug Delivery, 25, 376–387.
Dinanath, G., Padmini, K., Dipak, M., & Namdeo, J. (2017). Development of particulate mucoadhesive gel for intranasal delivery. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research, 10, 222.
Kritika, S., Bhupen, K., & Banasmita, K. (2016). Development of mucoadhesive microsphere-loaded intranasal gel. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research, 9, 139–144.
Balducci, A. G., Nastruzzi, C., Colombo, P., & Sonvico, F. (2013). Antidiuretic effect of desmopressin chimera agglomerates. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 440, 154–160.
Pringels, E., Callens, C., Vervaet, C., Dumont, F., Slegers, F., Foreman, P., & Remon, J. P. (2006). Influence of deposition and spray pattern of nasal powders on insulin bioavailability. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 310, 1–7.
Martignoni, I., Trotta, V., Lee, W. H., Loo, C. Y., Pozzoli, M., Young, P. M., Scalia, S., & Traini, D. (2016). Resveratrol solid lipid microparticles for nasal delivery. Journal of Microencapsulation, 33, 735–742.
Mosab, A. (2025). Approaches to achieve an oral controlled release drug delivery system using polymers: A recent review. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 7, 16–21.
Charlton, S. T., Davis, S. S., & Illum, L. (2007). Evaluation of bioadhesive polymers for nose-to-brain delivery. Journal of Controlled Release, 118, 225–234.
Giuliani, A., Balducci, A. G., Zironi, E., Colombo, G., Bortolotti, F., & Lorenzini, L. (2018). In vivo nose-to-brain delivery of ribavirin. Drug Delivery, 25, 376–387.
Deleu, D., & Hanssens, Y. (2000). Second-generation triptans in acute migraine therapy. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 40, 687–700.
Rudman, K. L., O’Brien, E. K., & Leopold, D. A. (2011). Radiographic distribution of drops and sprays. American Journal of Rhinology & Allergy, 25, 94–97.
Mustafa, E., Shaimaa, N. M., & Al, A. (2016). Design of zolmitriptan liquisolid orodispersible tablets. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 9, 297–303.
Pelgrim, G. J., Das, M., Haberland, U., Slump, C., Handayani, A., & Van Tuij, S. (2015). Development of an ex vivo beating heart model. Biomedical Research International, 2015, 1–8.
Kozlovskaya, L., Abou-Kaoud, M., & Stepensky, D. (2014). Quantitative analysis of drug delivery to the brain via nasal route. Journal of Controlled Release, 189, 133–140.
Thornton-Manning, J. R., & Dahl, A. R. (1997). Metabolic capacity of nasal tissue. Mutation Research, 380, 43–59.
Stevens, J., Ploeger, B. A., van der Graaf, P. H., Danhof, M., & de Lange, E. C. (2011). Nose-to-brain transport pharmacokinetic model. Drug Metabolism and Disposition, 39, 2275–2282.
Giuliani, A., Balducci, A. G., Zironi, E., Colombo, G., Bortolotti, F., Lorenzini, L., Galligioni, V., Pagliuca, G., Scagliarini, A., Calzà, L., & Sonvico, F. (2018). In vivo nose-to-brain delivery of ribavirin. Drug Delivery, 25, 376–387.
Hammarlund-Udenaes, M., de Lange, E., & Thorne, R. G. (2014). Pharmacokinetic concepts in brain drug delivery. In Drug delivery to the brain (pp. 127–161). Springer.
Lee, V. H. L. (1988). Enzymatic barriers to peptide and protein absorption. Critical Reviews in Therapeutic Drug Carrier Systems, 5, 69–97.
Rathananand, M., Kumar, D. S., Shirwaikar, A., Kumar, R., & Kumar, D. S. (2007). Preparation of mucoadhesive microspheres for nasal delivery. Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 69, 652–657.
Martin, E., Nicolaas, G. M., Schipper, J., Coos, V., & Frans, W. H. (1997). Nasal mucociliary clearance. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 29, 13–38.
McMartin, C., Hutchinson, L. E., Hyde, R., & Peters, G. E. (1987). Structural requirements for nasal absorption. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 76, 535–540.
Mestecky, J., Moldoveanu, Z., Michalek, S. M., Morrow, C. D., Compans, R. W., Schafer, D. P., & Russell, M. W. (1997). Vaccine delivery by mucosal routes. Journal of Controlled Release, 48, 243–257.
Ugwoke, M. I., Agu, R. U., Verbeke, N., & Kinget, R. (2005). Nasal mucoadhesive drug delivery. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 57, 1640–1665.
Morimoto, K., Miyazaki, M., & Kakemi, M. (1995). Effects of proteolytic enzyme inhibition. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 133, 1–8.
Mygind, N., & Vesterhauge, S. (1978). Aerosol distribution in the nose. Rhinology, 16, 79–88.
Newhouse, M. T. (1991). Advantages of pressurized metered-dose inhalers. Journal of Aerosol Medicine, 4, 139–150.
O’Hagan, D. T., & Illum, L. (1990). Absorption of peptides and proteins from the respiratory tract. Critical Reviews in Therapeutic Drug Carrier Systems, 7(1), 35–97.
Ohwaki, K., Ando, H., Watanabe, S., & Miyake, Y. (1985). Effects of dose, pH and osmolarity. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 74, 550–552.
Ramaprasad, Y. V. (1996). Intranasal drug delivery systems. Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 58, 1–8.
Sarkar, M. A. (1992). Drug metabolism in the nasal mucosa. Pharmaceutical Research, 9, 1–9.
Satish, B. B., Adhikrao, V. Y., Amelia, M. A., & Rajkumar, M. (2008). Bioavailability of intranasal drug delivery system. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutics, 201–215.
Soane, R. J., Frier, M., Perkins, A. C., Jones, N. S., Davis, S. S., & Illum, L. (1999). Evaluation of clearance characteristics of bioadhesive systems. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 178, 55–65.
Soane, R. J., Hinchcliffe, M., Davis, S. S., & Illum, L. (2001). Clearance characteristics of chitosan-based formulations. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 217, 183–191.
Striebel, H. W., Kramer, J., Luhmann, I., Rohierse-Hohler, I., & Rieger, A. (1993). Pharmacokinetics of intranasal fentanyl. Der Schmerz, 7, 122–125.
Downloads
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2026 Dr. Valikala Viswanath, P. Anitha, D. Swarnalatha, S. Chandana Priya, P. Poojitha, P. Varun Kumar, S.K. Farina, S. Mahabunnisa (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
License Terms
This is an open-access article published in the International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences and Technology (IJRPST) by Rubatosis Publications.
It is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, reproduction, and adaptation in any medium or format, provided the original author(s) and source are appropriately credited, a link to the license is provided, and any changes made are indicated.
To view a copy of this license, visit: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
For any further queries or permissions beyond the scope of this license, please contact: editor@rubatosis.org




