Contemporary approaches to the preparation of metal nanoparticles: methods and mechanistic insights
 DOI:
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33974/0pwpmq26
Keywords:
Nanomaterials, Nanoparticles, Nanocomposites, Nanoarchitectures, NanostructuresAbstract
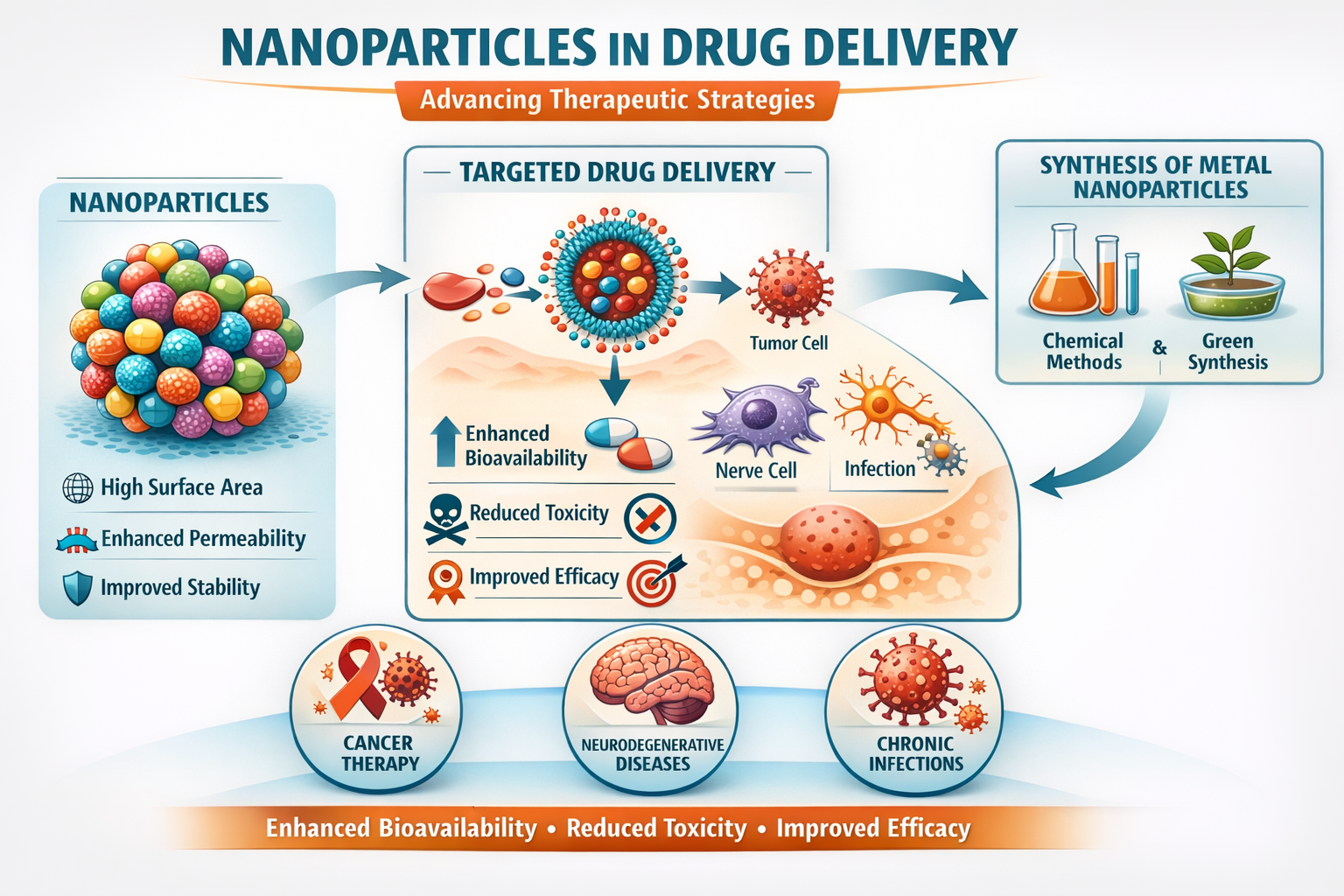
Nanoparticles have transformed drug delivery systems to provide new approaches to increase the dissolution, absorption, and targeting properties of drug molecules. They have a nanoscale structure that gives them special characteristics such as high surface area, enhanced membrane permeability and enhanced physicochemical stability in comparison with the traditional drug delivery systems. Such properties render the nanoparticles especially useful in treatment of such complicated illness as cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and chronic infectious diseases. This review paper focuses on the different ways of synthesizing metal nanoparticles and their pharmaceutical usage, as a way of overcoming the limitations of the conventional methods of delivery. Altogether, nanoparticles are characterized by enhanced stability and bioavailability, reduced toxicity, and a high possibility of benefiting therapeutic performance and safety in nanomedicine.
Downloads
References
Rai, M., Yadav, A., & Gade, A. (2009). Silver nano-particles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnology Advances, 27(1), 76–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.09.002
Burda, C., Chen, X., Narayanan, R., & El-Sayed, M. A. (2005). Chemistry and properties of nanocrys-tals of different shapes. Chemical Reviews, 105(4), 1025–1102. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr030063a
Morones, J. R., Elechiguerra, J. L., Camacho, A., Holt, K., Kouri, J. B., Ramírez, J. T., & Yacaman, M. J. (2005). The bactericidal effect of silver nano-particles. Nanotechnology, 16(10), 2346–2353. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/16/10/059
Dreaden, E. C., Alkilany, A. M., Huang, X., Murphy, C. J., & El-Sayed, M. A. (2012). The golden age: Gold nanoparticles for biomedicine. Chemical So-ciety Reviews, 41(7), 2740–2779. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1cs15237h
Ahmed, S., Ahmad, M., Swami, B. L., & Ikram, S. (2016). A review on plant extract mediated syn-thesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications. Journal of Advanced Research, 7(1), 17–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2015.02.007
Wang, X. Q., & Mujumdar, A. S. (2007). A review on nanofluids—Part I: Theoretical and numerical investigations. Brazilian Journal of Chemical En-gineering, 24(4), 613–630. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0104-66322007000400013
Das, S. K., Choi, S. U. S., Yu, W., & Pradeep, T. (2008). Nanofluids: Science and technology. Wiley.
Hasanpoor, M., Aliofkhazraei, M., & Delavari, H. (2015). Microwave-assisted synthesis of zinc ox-ide nanoparticles. Procedia Materials Science, 11, 320–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mspro.2015.11.101
Ayyub, P., Multani, M., Barma, M., Palkar, V. R., & Vijayaraghavan, R. (2001). Synthesis of nanocrys-talline material by sputtering and laser ablation at low temperatures. Applied Physics A, 73, 67–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003390100858
Shuaib, U., Ansari, M. A., Alzohairy, M. A., Alma-troudi, A., Khan, H. M., & Ahmad, A. (2020). Plas-ma-liquid synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their antibacterial and antifungal applications. Materials Research Express, 7(3), 035015. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab74a6
Ganjali, M., Vahdatkhah, P., & Marashi, S. M. B. (2015). Synthesis of Ni nanoparticles by pulsed laser ablation method in liquid phase. Procedia Materials Science, 11, 359–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mspro.2015.11.111
Kumar, C. V., & Pattammattel, A. (2017). Synthet-ic routes to graphene preparation from the per-spectives of possible biological applications. In In-troduction to graphene (pp. 17–44). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-811829-7.00002-4
Park, E., Park, H. W., & Lee, J. S. (2015). Synthesis of hierarchical copper oxide composites prepared via electrical explosion of the wire in liquids method. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 482, 710–717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2015.07.007
Peng, C., Wang, J., Zhou, N., & Sun, G. (2016). Fabrication of nanopowders by electrical explo-sion of a copper wire in water. Current Applied Physics, 16, 284–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2015.12.008
Han, R., Zhu, W., Wu, J., Li, C., Zhang, C., Cui, R., et al. (2020). Spatial–temporal evolution of plasma radiation in electrical wire explosion. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 53, 345201. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/ab8c3a
Liu, Z., Qian, D., Xu, C., Li, L., Zou, X., & Wang, X. (2022). Unbalanced distribution of electric cur-rent in underwater electrical wire array explo-sion. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 55, 185205. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/ac54d4
Fiévet, F., Ammar-Merah, S., Brayner, R., Chau, F., Giraud, M., Mammeri, F., et al. (2018). The polyol process: A unique method for easy access to metal nanoparticles with tailored sizes, shapes and compositions. Chemical Society Reviews, 47, 5187–5233. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CS00777A
Tartaro, G., Mateos, H., Schirone, D., Angelico, R., & Palazzo, G. (2020). Microemulsion microstruc-ture(s): A tutorial review. Nanomaterials, 10(9), 1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091657
Tian, Y., Zhou, J., He, C., He, L., Li, X., & Sui, H. (2022). The formation, stabilization and separa-tion of oil–water emulsions: A review. Nano-materials, 12(4), 738. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12040738
Arnal, P., Corriu, R. J. P., Leclercq, D., Mutin, P. H., & Vioux, A. (2002). Preparation of transition met-al oxides by a nonhydrolytic sol–gel process. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 12, 2095–2104. https://doi.org/10.1039/B202780H
Cargnello, M., Gordon, T. R., & Murray, C. B. (2014). Solution-phase synthesis of titanium diox-ide nanoparticles and nanocrystals. Chemical Re-views, 114(19), 9319–9345. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr500170p
Sun, S., Zeng, H., Robinson, D. B., Raoux, S., Rice, P. M., Wang, S. X., & Li, G. (2011). Monodisperse magnetic nanoparticles for theranostic applica-tion. Accounts of Chemical Research, 44(10), 875–882. https://doi.org/10.1021/ar200084b
Das, M., & Chatterjee, S. (2019). Green synthesis, characterization and applications of nanoparti-cles. In Green synthesis of metal/metal oxide na-noparticles toward biomedical applications (pp. 265–301). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-814373-2.00012-8
Gurunathan, S., Han, J. W., Eppakayala, V., & Kim, J. H. (2014). A green chemistry approach for syn-thesizing biocompatible gold nanoparticles. Na-noscale Research Letters, 9, 248. https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-9-248
Xiang, H., Meng, J., Shao, W., Zeng, D., Ji, J., Wang, P., et al. (2023). Plant protein-based self-assembling core–shell nanocarrier for effectively controlling plant viruses. Chemical Engineering Journal, 464, 142432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.142432
Mittal, A. K., Chisti, Y., & Banerjee, U. C. (2013). Synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant extracts. Biotechnology Advances, 31, 346–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.01.003
Chaudhary, R., Nawaz, K., Khan, A. K., Hano, C., Abbasi, B. H., & Anjum, S. (2020). An overview of the algae-mediated biosynthesis of nanoparticles and their biomedical applications. Biomolecules, 10(11), 1498. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10111498
Gour, A., & Jain, N. K. (2019). Advances in green synthesis of nanoparticles. Artificial Cells, Nano-medicine, and Biotechnology, 47(1), 844–851. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2019.1577878
Mukherjee, P., Ahmad, A., Mandal, D., Senapati, S., Sainkar, S. R., Khan, M. I., et al. (2001). Fungus-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their immobilization in the mycelial matrix. Nano Letters, 1(10), 515–519. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl0155274
Lee, H. L., Lytton-Jean, A. K. R., Chen, Y., Love, K. T., Park, A. I., Karagiannis, E. D., et al. (2012). Mo-lecularly self-assembled nucleic acid nanoparti-cles for targeted in vivo siRNA delivery. Nature Nanotechnology, 7(6), 389–393. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2012.73
Akbarian, M., Mahjoub, S., Elahi, S. M., Zabihi, E., & Tashakkorian, H. (2020). Green synthesis, for-mulation and biological evaluation of a novel ZnO nanocarrier loaded with paclitaxel. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 186, 110686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110686
Castro, L., Blázquez, M. L., Muñoz, J. A., González, F., & Ballester, A. (2013). Biological synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using algae. IET Nanobi-otechnology, 7, 109–116. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-nbt.2012.0041
Malik, S., Muhammad, K., & Waheed, Y. (2023). Nanotechnology: A revolution in modern indus-try. Molecules, 28(2), 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020661
Jamkhande, P. G., Ghule, N. W., Bamer, A. H., & Kalaskar, M. G. (2019). Metal nanoparticles syn-thesis: An overview on methods, advantages and disadvantages, and applications. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 53, 101174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2019.101174
Salem, S. S. (2023). A mini review on green nano-technology and its development in biological ef-fects. Archives of Microbiology, 205(4), 128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03409-8
Alqarni, L. S., Alghamdi, M. D., Alshahrani, A. A., & Nassar, A. M. (2022). Green nanotechnology: Re-cent research on bioresource‐based nanoparticle synthesis and applications. Journal of Chemistry, 2022, 4030999. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/4030999
Scallan, E., Hoekstra, R. M., Angulo, F. J., Tauxe, R. V., Widdowson, M. A., Roy, S. L., et al. (2011). Foodborne illness acquired in the United States—Major pathogens. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 17(1), 7–15. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid1701.P11101
Havelaar, A. H., Kirk, M. D., Torgerson, P. R., et al. (2015). World Health Organization global esti-mates and regional comparisons of the burden of foodborne disease. PLoS Medicine, 12(12), e1001923. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001923
Cedervall, T., Lynch, I., Lindman, S., Berggård, T., Thulin, E., Nilsson, H., et al. (2007). Understand-ing the nanoparticle–protein corona using meth-ods to quantify exchange rates and affinities of proteins for nanoparticles. Proceedings of the Na-tional Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104(7), 2050–2055. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0608582104
Lynch, I., & Dawson, K. A. (2008). Protein–nanoparticle interactions. Nano Today, 3(1–2), 40–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1748-0132(08)70014-8
Monopoli, M. P., Åberg, C., Salvati, A., & Dawson, K. A. (2012). Biomolecular coronas provide the biological identity of nanosized materials. Nature Nanotechnology, 7, 779–786. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2012.207
Liu, R., Jiang, W., Walkey, C. D., Chan, W. C. W., & Cohen, Y. (2019). Nanoparticles as biomarker harvesting agents: The emerging role of nanopar-ticle–protein corona. ACS Nano, 13(4), 3165–3175. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b08508
Deng, Z. J., Liang, M., Monteiro, M., Toth, I., & Minchin, R. F. (2009). Nanoparticle–protein in-teractions: Toward predicting the structure of the protein corona. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 131(27), 9490–9500. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja903186k
Mirkin, C. A., Letsinger, R. L., Mucic, R. C., & Storhoff, J. J. (1996). A DNA-based method for ra-tionally assembling nanoparticles into macro-scopic materials. Nature, 382, 607–609. https://doi.org/10.1038/382607a0
Taton, T. A., Mirkin, C. A., & Letsinger, R. L. (2000). Scanometric DNA array detection with nanoparticle probes. Science, 289, 1757–1760. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.289.5485.1757
Zhang, L., & Webster, T. J. (2009). Nanotechnolo-gy and nanomaterials: Promises for improved tis-sue regeneration. Nano Today, 4(1), 66–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2008.10.014
Dvir, T., Timko, B. P., Kohane, D. S., & Langer, R. (2011). Nanotechnological strategies for engi-neering complex tissues. Nature Nanotechnology, 6, 13–22. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2010.246
Rezwan, K., Chen, Q. Z., Blaker, J. J., & Boccaccini, A. R. (2006). Bioceramics and bioglass composites for tissue engineering. Biomaterials, 27, 3413–3431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.01.039
Peer, D., Karp, J. M., Hong, S., Farokhzad, O. C., Margalit, R., & Langer, R. (2007). Nanocarriers as an emerging platform for cancer therapy. Nature Nanotechnology, 2, 751–760. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2007.387
Blanco, E., Shen, H., & Ferrari, M. (2015). Princi-ples of nanoparticle design for overcoming bio-logical barriers. Nature Biotechnology, 33, 941–951. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3330
Sahoo, S. K., & Labhasetwar, V. (2003). Nanotech approaches to drug delivery and imaging. Journal of Controlled Release, 100, 1–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-3659(04)00129-1
Kim, B. H., Lee, N., Kim, H., et al. (2018). Nano-particle contrast agents for MRI. Chemical Re-views, 118, 9326–9387. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00134
Na, H. B., Song, I. C., & Hyeon, T. (2009). Inorgan-ic nanoparticles for MRI contrast agents. Ad-vanced Materials, 21, 2133–2148. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200802366
Pankhurst, Q. A., Connolly, J., Jones, S. K., & Dob-son, J. (2003). Applications of magnetic nanopar-ticles in biomedicine. Journal of Physics D: Ap-plied Physics, 36, R167–R181. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/36/13/201
Downloads
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2026 Dr. Valikala Viswanath, D. Swarnalatha, Dr. P. Anitha, V. Haripriya, S. Soniya, K. Vanitha, P. Pavani, S. Yuvaraj (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
License Terms
This is an open-access article published in the International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences and Technology (IJRPST) by Rubatosis Publications.
It is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, reproduction, and adaptation in any medium or format, provided the original author(s) and source are appropriately credited, a link to the license is provided, and any changes made are indicated.
To view a copy of this license, visit: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
For any further queries or permissions beyond the scope of this license, please contact: editor@rubatosis.org




